Are you interested in finding '3 3 implicit differentiation homework'? Here you can find all of the details.
Table of contents
- 3 3 implicit differentiation homework in 2021
- Implicit differentiation calculator
- Implicit differentiation questions and answers pdf
- Implicit differentiation pdf
- Implicit differentiation worksheet with solutions
- Implicit differentiation worksheet pdf
- Chain rule and implicit differentiation worksheet
- Implicit differentiation calculator with steps
3 3 implicit differentiation homework in 2021
 This picture shows 3 3 implicit differentiation homework.
This picture shows 3 3 implicit differentiation homework.
Implicit differentiation calculator
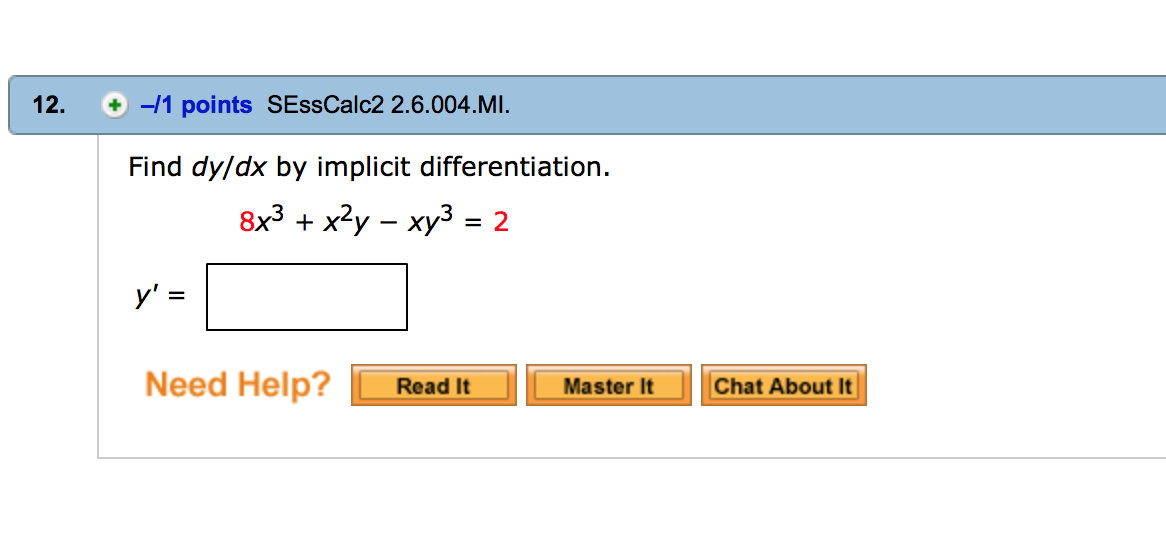 This picture illustrates Implicit differentiation calculator.
This picture illustrates Implicit differentiation calculator.
Implicit differentiation questions and answers pdf
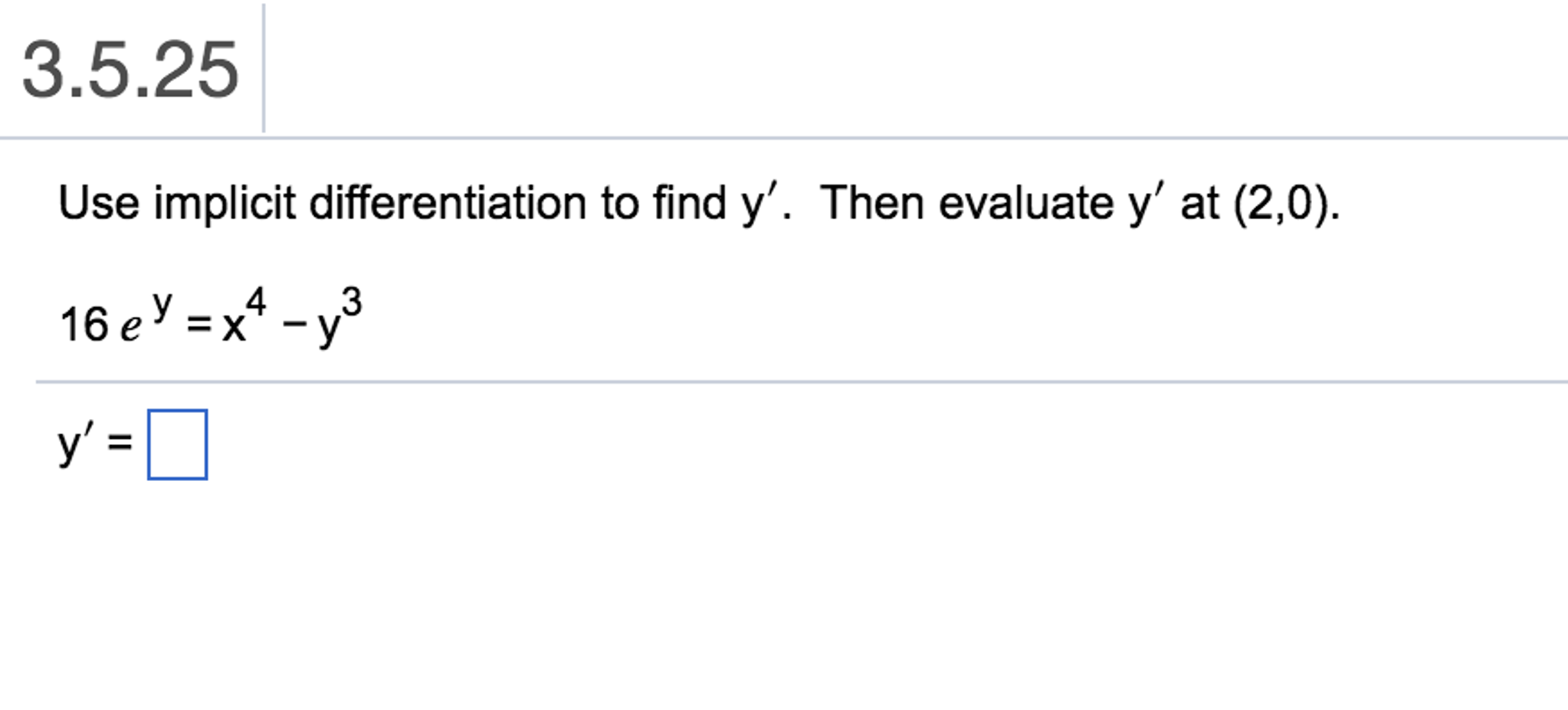 This picture shows Implicit differentiation questions and answers pdf.
This picture shows Implicit differentiation questions and answers pdf.
Implicit differentiation pdf
 This picture demonstrates Implicit differentiation pdf.
This picture demonstrates Implicit differentiation pdf.
Implicit differentiation worksheet with solutions
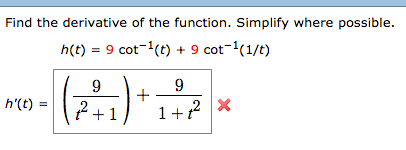 This picture representes Implicit differentiation worksheet with solutions.
This picture representes Implicit differentiation worksheet with solutions.
Implicit differentiation worksheet pdf
 This image demonstrates Implicit differentiation worksheet pdf.
This image demonstrates Implicit differentiation worksheet pdf.
Chain rule and implicit differentiation worksheet
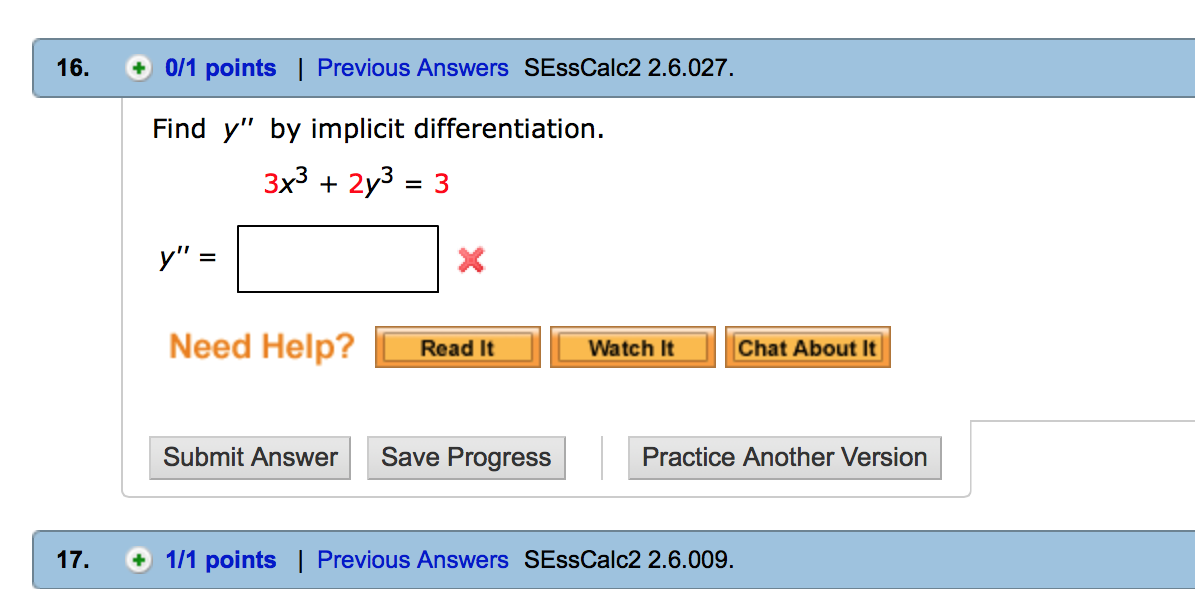 This image representes Chain rule and implicit differentiation worksheet.
This image representes Chain rule and implicit differentiation worksheet.
Implicit differentiation calculator with steps
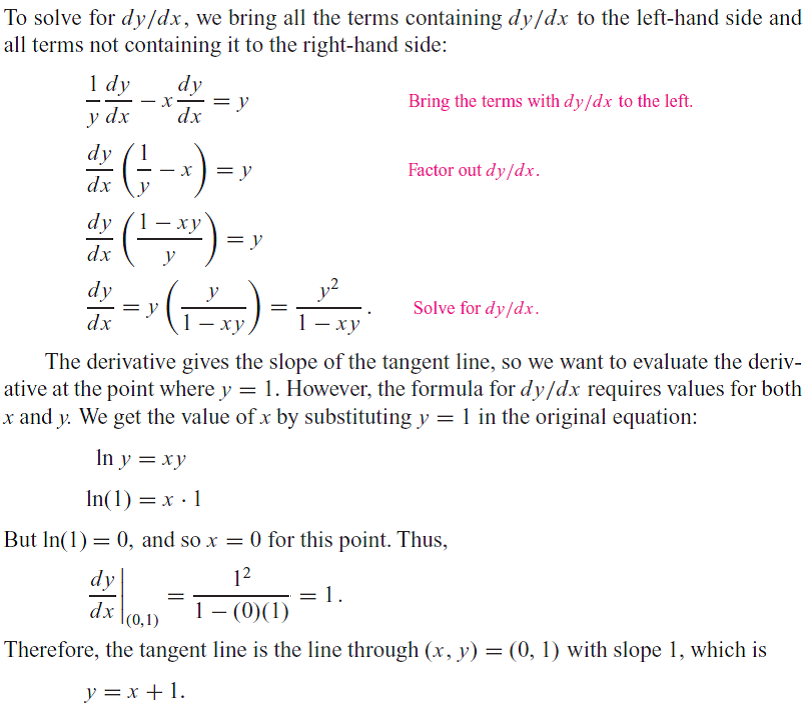 This image representes Implicit differentiation calculator with steps.
This image representes Implicit differentiation calculator with steps.
Which is an example of implicit differentiation in calculus?
For example, the equation y−x2 = 1 y − x 2 = 1 defines the function y = x2 +1 y = x 2 + 1 implicitly. Implicit differentiation allows us to find slopes of tangents to curves that are clearly not functions (they fail the vertical line test).
How to find the folium of Descartes curve?
Find the equation of the line tangent to the graph of y3+x3 −3xy =0 y 3 + x 3 − 3 x y = 0 at the point (3 2, 3 2) ( 3 2, 3 2) ( (Figure) ). This curve is known as the folium (or leaf) of Descartes. Figure 3.
How to calculate the differentiation of D Y D X?
Take the derivatives, so d d x ( x 2) = 2 x and d d x ( y 2) = 2 y d y d x. 2 y d y d x = − 2 x Step 2. Keep the terms with d y d x on the left. Move the remaining terms to the right. d y d x = − x y Step 4. Divide both sides of the equation by 2 y.
Last Update: Oct 2021